Introduction
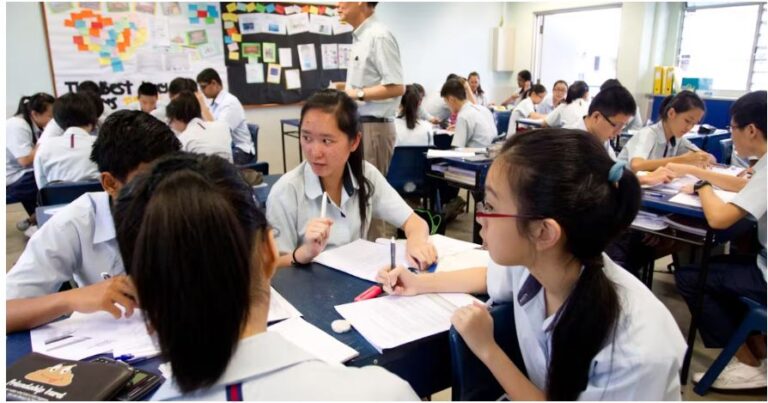
Did you know that Singapore consistently ranks at the top in international math assessments? This success is no accident, and one key factor is the emphasis on innovative teaching methods, particularly interactive learning. For students receiving primary math tuition, interactive learning can make a significant difference, turning math from a challenging subject into an engaging and enjoyable experience. This article explores the best practices for enhancing primary math education through interactive learning, ensuring that students are both engaged and well-prepared.
I. Understanding Interactive Learning
Definition and Concepts
Interactive learning is an educational approach that involves active student participation through engaging activities, discussions, and hands-on experiences. This method contrasts with traditional passive learning, where students merely listen and take notes. Interactive learning encourages critical thinking, problem-solving, and collaboration, making learning more dynamic and effective.
Importance in Math Education
Interactive learning is especially crucial for primary math students, as it helps demystify complex concepts and makes math enjoyable. In Singapore, educational goals emphasize critical thinking and problem-solving, skills that interactive learning naturally enhances. By making math relatable and fun, students are more likely to develop a lasting interest in the subject.
II. Current State of Primary Math Education in Singapore
Overview of Singapore’s Math Curriculum
Singapore’s primary math curriculum is renowned for its structured and progressive approach. It focuses on building a strong foundation in basic arithmetic, problem-solving, and logical reasoning. The curriculum is designed to be challenging yet accessible, ensuring that students grasp fundamental concepts before moving on to more complex topics.
Role of Interactive Learning
Interactive learning is well-integrated into Singapore’s math curriculum. Schools utilize various tools and methods to create an engaging learning environment. Government and educational initiatives, such as the Singapore Math method, promote interactive techniques that help students understand and apply math concepts effectively.
III. Best Practices for Interactive Learning in Primary Math
Use of Technology
Educational Apps and Software
Educational apps like “Mathletics” and “Koobits” are popular in Singaporean classrooms. These apps offer interactive exercises and games that make learning math fun and engaging. They provide instant feedback, allowing students to learn at their own pace.
Interactive Whiteboards and Tablets
Interactive whiteboards and tablets transform traditional lessons into dynamic, interactive experiences. Teachers can illustrate math problems visually, making it easier for students to grasp abstract concepts. These tools also facilitate group activities and interactive problem-solving sessions.
Hands-On Activities
Manipulatives
Manipulatives, such as counting blocks, abacuses, and geometric shapes, are essential tools in teaching math concepts. They provide a tangible way for students to explore and understand abstract ideas, making learning more concrete and memorable.
Math Games
Games like “Math Bingo” and “Number Puzzles” are excellent for reinforcing math skills. These activities make learning enjoyable and help students practice math in a playful and stress-free environment.
Collaborative Learning
Group Work
Group activities and projects encourage students to work together, fostering teamwork and communication skills. Collaborative learning helps students learn from each other and develop a deeper understanding of math concepts.
Peer Tutoring
Peer tutoring is an effective method where students help each other learn. It builds confidence in both the tutor and the tutee, creating a supportive learning environment.
Real-World Applications
Problem-Solving Tasks
Applying math to real-life scenarios helps students see the relevance of what they are learning. Tasks such as budgeting for a class event or measuring ingredients for a recipe make math practical and engaging.
Field Trips and Practical Experiences
Field trips to places like science centers or interactive museums provide hands-on learning experiences. These trips allow students to see math in action and understand its real-world applications.
Personalized Learning
Adaptive Learning Programs
Software like “DreamBox” adapts to each student’s learning pace, providing customized lessons that cater to individual needs. This personalized approach helps ensure that all students can progress at a comfortable rate.
Individualized Feedback
Tailored feedback is crucial for student growth. Teachers can use assessments and observations to provide specific guidance, helping students understand their strengths and areas for improvement.
IV. Case Studies and Success Stories
Examples from Singaporean Schools
Several schools in Singapore have successfully implemented interactive learning strategies. For example, at XYZ Primary School, students use interactive whiteboards daily, leading to significant improvements in math test scores. Teachers at ABC Primary School have reported higher student engagement and enthusiasm for math since introducing educational apps and games.
Teacher and Student Testimonials
Teachers and students have shared positive feedback about interactive learning. One teacher noted, “Interactive learning has transformed my classroom. Students are more engaged and excited about math.” A student commented, “I used to find math boring, but now it’s my favorite subject because we get to play games and use cool apps.”
V. Challenges and Solutions
Common Challenges
Implementing interactive learning can come with challenges, such as limited resources, lack of teacher training, and varying student abilities.
Strategies to Overcome Challenges
To overcome these obstacles, schools can invest in teacher training programs, seek funding for educational technology, and implement differentiated instruction strategies to cater to diverse learning needs.
VI. Future Trends in Interactive Learning
Technological Advancements
As technology continues to evolve, new tools and platforms will emerge, further enhancing interactive learning. Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) are poised to revolutionize how students experience math, making learning even more immersive and engaging.
Innovative Teaching Methods
Emerging pedagogical approaches, such as gamification and blended learning, are set to transform traditional teaching methods. These innovations will continue to make math education more interactive and effective.
Policy and Educational Reforms
Anticipated changes in educational policy may further support interactive learning. Initiatives aimed at integrating more technology into classrooms and promoting innovative teaching methods will likely become more prevalent.
Conclusion
Interactive learning is a powerful tool in engaging primary math students in Singapore. By incorporating technology, hands-on activities, collaborative learning, real-world applications, and personalized learning, educators can create a dynamic and effective math learning environment.
The long-term benefits of interactive learning are immense. It not only helps students understand math concepts better but also fosters a love for learning that lasts a lifetime.